Google Sends Parents of LGBTQ Kids to Conversion Therapy Websites. Why?
We asked Americans to Google five queries looking for resources for LGBTQ people who are struggling. Far-right religious groups dominated the results.
Google is the most powerful search engine in the world, commanding nearly 90% of the global search engine market and generating over $348 billion in revenue last year. Over half of Americans say they trust Google more than their formal education.
But how does Google's algorithm decide which results show up? And how do these results influence LGBTQ kids, their parents and Americans at large who are searching for help?
Uncloseted Media asked five Americans from around the country to Google five common queries related to LGBTQ identity, religion and parenting.
The results were alarming and raised an urgent question: With nearly 40% of LGBTQ youth seriously considering suicide just last year, what happens when a queer teen or the parent of a gay kid in crisis turns to Google?

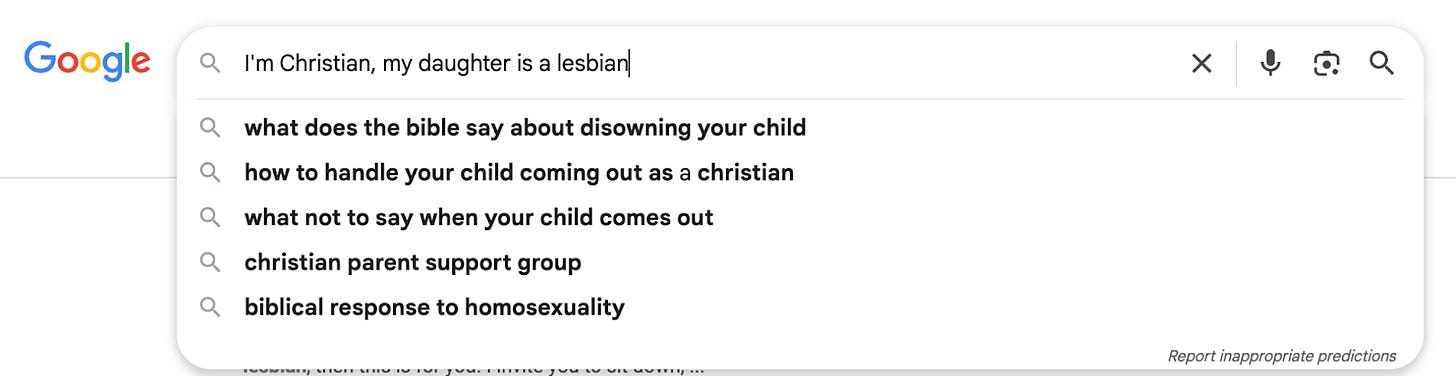
“I’m Christian, my daughter is a lesbian,” Melanie Brown, a Southern Baptist from High Point, North Carolina, types into Google.
When Brown presses enter, Bible Bulletin Board comes up as the third result, with the suggestion of “offering hope for change,” and “lead[ing] the way to the alternative to homosexuality.” It goes on to explain that “homosexuality is contrary to God’s Word. It is sin and as always results in sin’s destructive effects on the individual and on those close to them.”
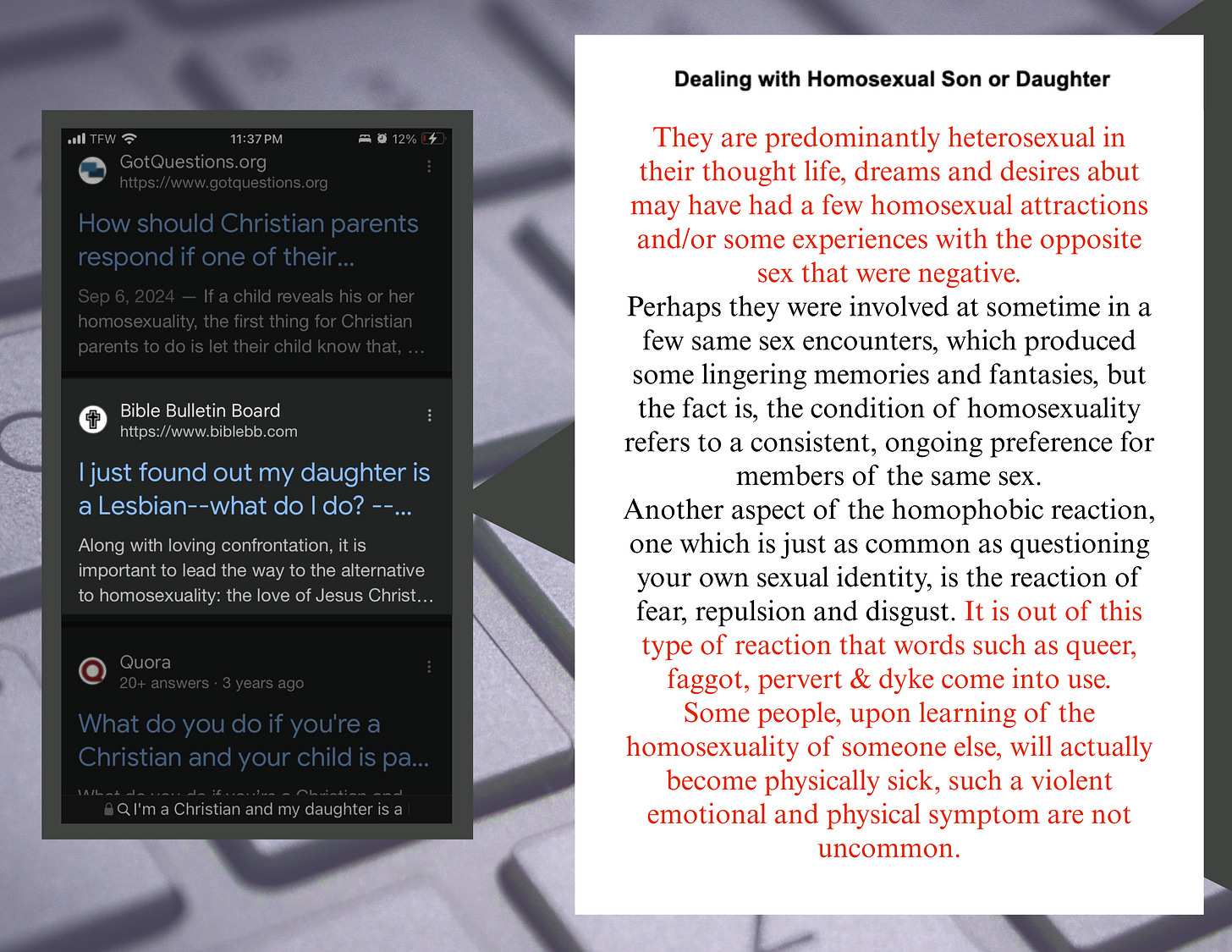
In the living room, Brown's 15-year-old daughter Genna, with her dog on her lap, Googles “accurate information on gay kids and what to do.”
Focus on the Family (FOTF) is the first result. She clicks the link and lands on the platform of a hyper-religious organization known for promoting conversion therapy and labeling her sexuality as sinful.
The site, which presents itself as a reputable religious source, features a tab titled “Understanding Homosexuality” and a section under their resources for “Homosexuality.” It states: “[FOTF] is committed to upholding God’s design for the expression of human sexuality: a husband and wife in a marriage.”
It offers suggested reading on “redemption” from a gay lifestyle, along with 11 counseling resources aimed at changing sexual orientation, including The Alliance for Therapeutic Choice and Scientific Integrity, which guarantees “professional assistance … for persons who experience unwanted homosexual attractions.”
The language is intentionally padded, which means Genna and her mom—and many of the other millions of Christian parents of queer kids—may never know that Google led them to a Southern Poverty Law Center-designated anti-LGBTQ hate group. FOTF is known for its long-standing opposition to LGBTQ rights, for spreading anti-LGBTQ disinformation and for framing homosexuality and transgender identity as sinful and disordered.
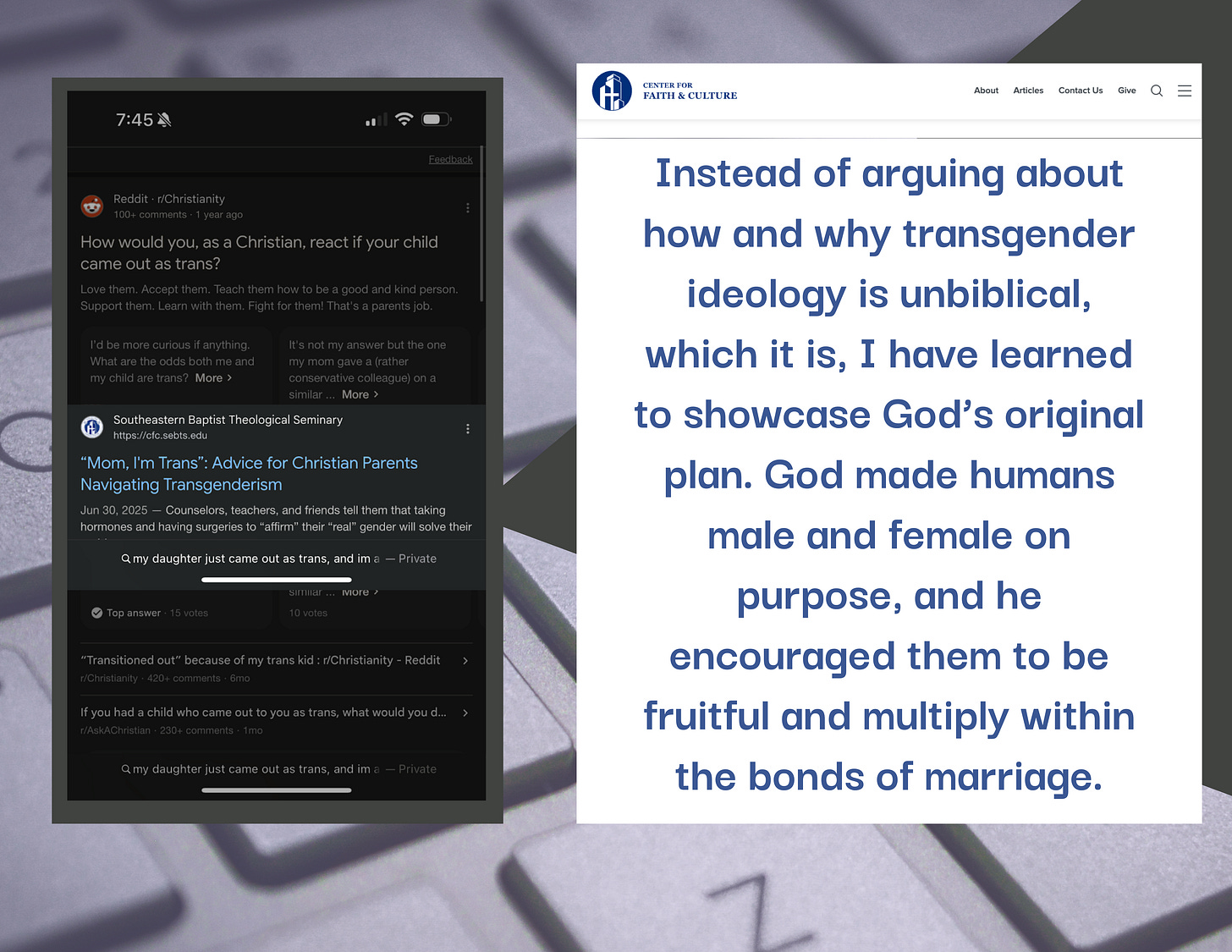
In South Boston, Virginia, Tommy O’Neil Googles, “My daughter just came out as trans and I’m a Christian.” As a father of two, he wants what’s best for his kids. According to Southeastern Baptist Theological Seminary, Google’s second result, O’Neil should recognize that God doesn't make mistakes when assigning sex and give sympathy for those who are indoctrinated in the “transgender cult.”
What O’Neil might not know is that this seminary made the list of Worst Campuses for LGBTQ students. And in 2016, it was granted an exemption to Title IX, allowing it to discriminate against LGBTQ students for religious reasons.
Thousands of miles away in Anchorage, Alaska, 38-year-old bisexual woman April Samberg Googles, “I am bisexual and have a husband who is Christian, am I going to hell?”
The third result is once again an article by FOTF that tells April that “same-sex-attracted strugglers” and “transgender and homosexual lust and behavior are wrong.”
In Cincinnati, 44-year-old Mark Just Googles, “accurate information on homosexual kids and what to do.” FOTF is the top search result.
“I don't feel good about it,” Just told Uncloseted Media. “It's disturbing because if there are people out there who want to accept and understand their children or loved ones, this is what they're being pointed to.”
“[I feel] fear for the queer kids with Christian parents who will be seeing that and thinking it’s good advice, and sorrow for the kids with parents who already have,” says Genna Brown, who was a “self-loathing, suicidal kid” who thought God would punish her for being gay before she came out to her now accepting parents. “It’s pretty awful that this is what’s being pushed for advice. This has no doubt harmed people.”
Uncloseted Media also asked folks in Taiwan, Lebanon, China, Hong Kong, Canada and India to Google similar queries. All of them had FOTF turn up as a top search result.
Why Does Google Allow This?
Google, like other search engines, compiles information and directs users to various websites by referencing the titles of web pages that it judges to be most reflective of what was searched.
“Google's algorithm is notoriously a black box,” says Jesse Ringer, founder of Method and Metric, a search engine optimization (SEO) growth company. “That's intentional to keep their competitive advantage.”
What we do know is that Google ranks search results by first crawling the web with an automated program called “spiders” to follow links from page to page and collect data.
It uses text matching to identify documents that it thinks are relevant to a query and then ranks them based on a combination of popularity, freshness, location and previous links clicked.
But for people searching for reliable information, its process can be problematic.
“Google doesn’t rank based on accuracy, but on popularity and query matching,” says Dirk Lewandowski, professor of information research and retrieval at the Hamburg University of Applied Sciences. “This is based on clicks and a network of how many other links are directed to this website. … Of course, users click what is shown in the first position. So we have kind of a rich get richer.”
How to Get a High Ranking
As websites with the highest rankings continue to receive more clicks, websites like FOTF can also employ other tactics to keep their prominent placement.
Backlinking—the process of having other web pages hyperlink back to your site—is one of the ways to maintain your high ranking.
“Backlinks are a big part of popularity. So the relationship between other websites linking to this source is a big part of Google's algorithm,” says Ringer. “There are SEO businesses that build link farms so that the content of their clients can go higher. They create a network effect and they link to each other. It is not unreasonable to think that [FOTF] has hired either an SEO person or they've hired an external agency to contribute to that.”
According to Francesca Tripodi, assistant professor at the University of North Carolina School of Information and Library Science, ranking can also be gamed by matching keywords to content. Tripodi looked at the metadata of progressive and conservative companies and found that conservative content creators “are much better at doing this.”
“They are savvy at creating new sets of words and tagging their content with them,” she says. “That's not something I'm seeing with progressive content creators.”
Tripodi says that not only does conservatism thrive online, it might be the only perspective returned.
“They are well-funded companies with large production budgets and effective digital marketing teams,” she wrote in a 2019 testimony about conservatism and Google searches. “This is why when you search for liberal phrases like ‘gender identity’ or ‘social justice’ the top returns … are conservative content creators.”
Google declined to speak on record with Uncloseted Media for this story.
In an email, a spokesperson said: “Like any search engine, Google indexes the content that’s available on the open web, relying on systems like keyword matching to surface relevant results. We are largely guided by local law when it comes to removing pages from search results.”
What If It’s Harmful or Illegal?
The United States notoriously protects harmful or misleading content—including anti-LGBTQ hate speech—under the First Amendment.
“The situation in [other countries] is a bit different than in America,” Lewandowski says. “For instance, Holocaust denial is illegal in Germany. So Google bans these sites, but they don't ban them in the U.S.”
Section 230 of the U.S. law protects Americans’ freedom of expression online by implying that we should all be responsible for our own actions and statements on the internet. This law largely takes legal pressure off of Google.
And in 2003, an Oklahoma court ruled that Google's rankings are subjective opinions and thus constitutionally protected.
Google’s policies for tamping down on harmful content “don't apply to web results.” Thus, there is little moderation on the web pages that pop up for Americans who use the search engine.
The spokesperson for Google says that “[they] hold themselves to a high standard when it comes to legal requirements to remove pages from Google search results” and that “they don’t remove web results except for child sexual abuse, highly personal information, spam, site owner requests, and valid legal requests.”
But according to the company, “determining whether content is illegal is not always a determination that Google is equipped to make.”
Tripodi says this might be why groups like FOTF are still showing up, even though conversion therapy is illegal in 23 states. She says these groups may have found a loophole in Google’s policy by “tricking” the search engine into thinking they are providing “resources” and not simply a recommendation for conversion therapy.
What Can Google Do to Fix This?
“Google has a responsibility for what is coming up in their results because people trust [them],” says Lewandowski. “They think something is correct or accurate because it is number one in Google.”
Fifteen-year-old Genna Brown is one of the 85% of Americans who feel this way, according to a 2025 study.
“Isn’t the first result typically ranked most credible?” she says. “Because I typically trust the first result more.”
“It’s pretty concerning what comes up when you search for these things,” Ringer says. “There needs to be more done to educate the people who are doing the searches on understanding news and information.”
But vulnerable groups, like LGBTQ kids who are living in households where they are told they are going to hell and parents who are often confused and in crisis themselves, are being led by Google’s algorithm to believe that being queer is wrong.
“1000% yes, these results concern me,” says Genna Brown. “We’re talking about organizations that promote practices like conversion therapy, which is insane. … I wish there was some disclaimer. Like, ‘Google has determined this to be a subjective query. As such, we can’t verify the following results. Proceed with caution.’”
Tripodi says she thinks consumers are responsible for about 20% of the burden by researching and verifying the sources they learn from. But she agrees with Brown in that Google carries an ethical responsibility for the content it chooses to rank and promote.
“As a global corporation that gobbles up all other possibilities for information, Google has a responsibility to ensure that its content is accurate and not harmful,” Tripodi says. “[It’s their job] to ensure that the information that they surface is accurate and reliable because we know people trust that information.”
Uncloseted Media reached out to Focus on the Family, Southeastern Baptist Theological Seminary, and Bible Bulletin Board. They did not respond to our request for comment.
Additional reporting by Sophie Holland and Spencer Macnaughton.
If objective, nonpartisan, rigorous, LGBTQ-focused journalism is important to you, please consider making a tax-deductible donation through our fiscal sponsor, Resource Impact, by clicking this button:





I can’t understand how we can live in 21st century and still some people think that different sexuality is a “sickness”? This is insane.
Really, my Google ads console tells the same story as your reporting. Thanks again for spreading the word!